What is an Active Directory (AD) Domain?
An Active Directory (AD) Domain is a fundamental organizational unit in Microsoft Windows network environments that serves as a centralized system for managing and securing network resources, user accounts, and network configurations. It is a hierarchical structure that allows system administrators to create and manage user profiles, implement security policies, and control access to network resources across an entire organization.
Key characteristics of an Active Directory Domain include:
- Centralized Authentication: The domain provides a single login and authentication point for users, allowing them to access various network resources with a single set of credentials.
- Organizational Structure: Domains are organized into logical hierarchies, typically consisting of domains, organizational units (OUs), and groups, which help manage users, computers, and network resources efficiently.
- Group Policy Management: Administrators can create and enforce group policies that define security settings, software installation, desktop configurations, and other network-wide parameters.
- Security and Access Control: The domain controller manages user permissions, access rights, and security policies, ensuring users can only access resources appropriate to their role and authorization level.
- Scalability: Domains can be structured in complex configurations like forests and trees, allowing organizations to manage large, geographically distributed networks with multiple domains.
Lab Prerequisite
- Pre-built Windows Server 2022 Virtual Machine
Network Configuration
I will assign VMnet4 to my Windows Server Network Adapter.
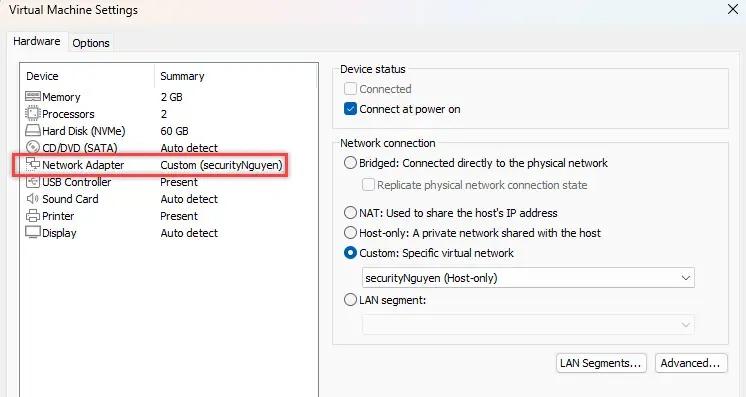
VMnet4 will have an IP address range of 192.168.10.0/24, and DHCP will be disabled. I was planning to allow my firewall to control the DHCP OR have another Windows Server that can run DHCP.
From my experience, it's very common for corporations to have multiple of multiple Domain Controllers.
Optional: Install VMware Tool
I like to install the VMware tool when I first log into a Virtual Machine. Why?
- Access to Full-Screen Resolution.
- Access to Copy & Paste.
If you don't know how to install VMware Tools on your virtual machine, Check out my guide on "How to Install the VMware Tool"
Step 1: Install Server Roles
On your screen, you should have Server Manager in front of you. If not, you can access it by going to the search bar and type: "Server Manager".
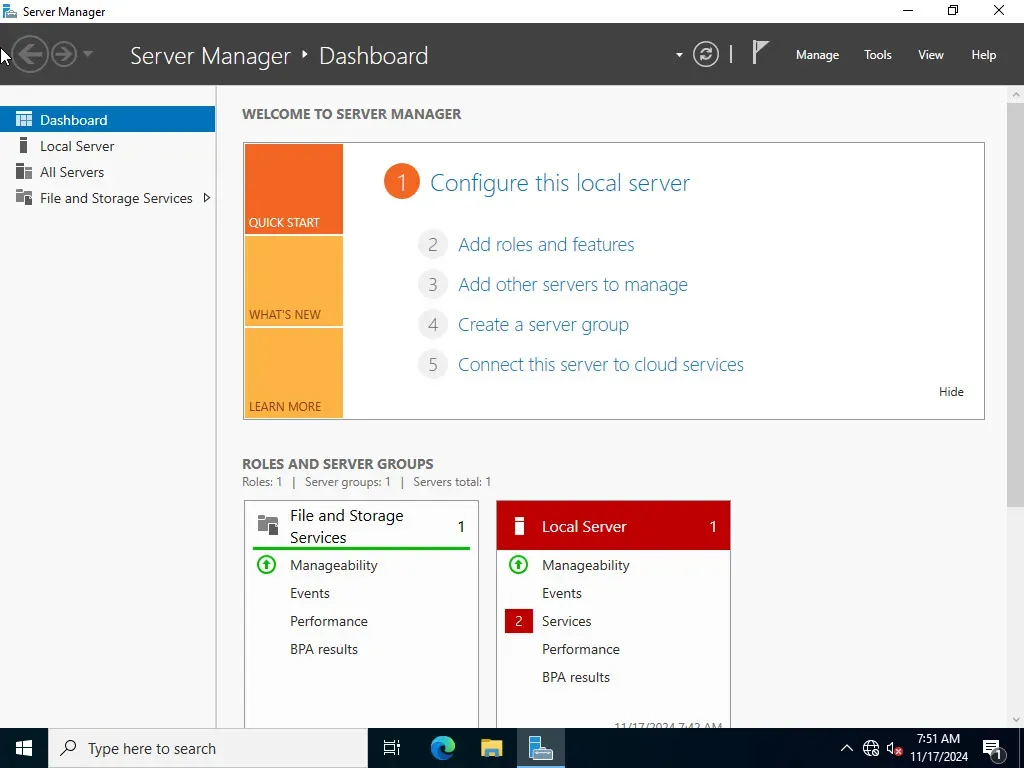
Next, we will select "Manage" -> "Add Roles and Features"
Add Roles and Features wizard will pop up
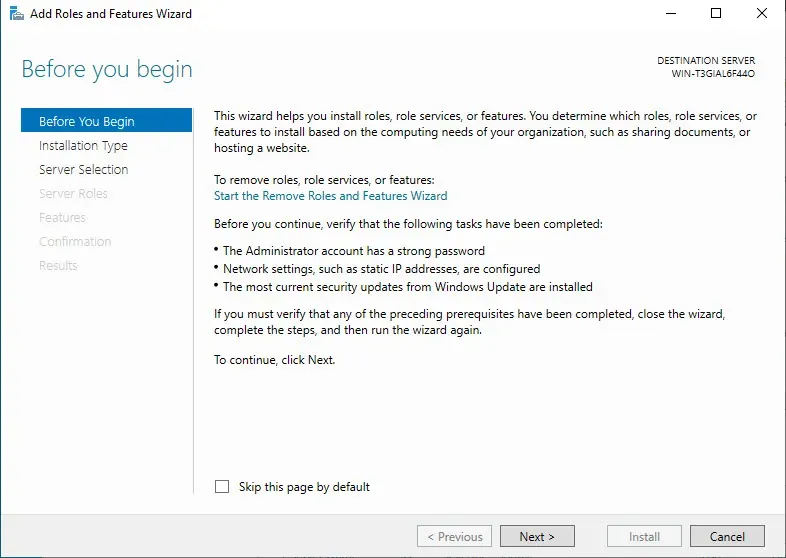
Click "Next" -> Installation Type: "Role-based or Feature-based installation" -> Click Next.
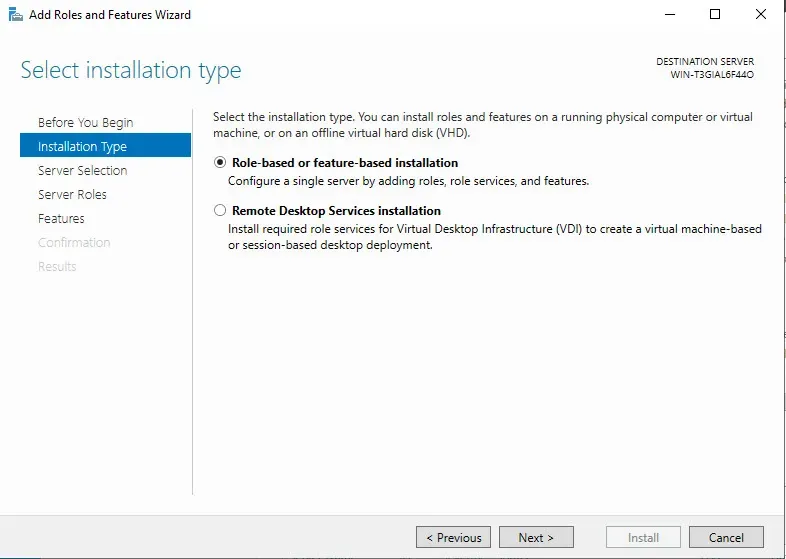
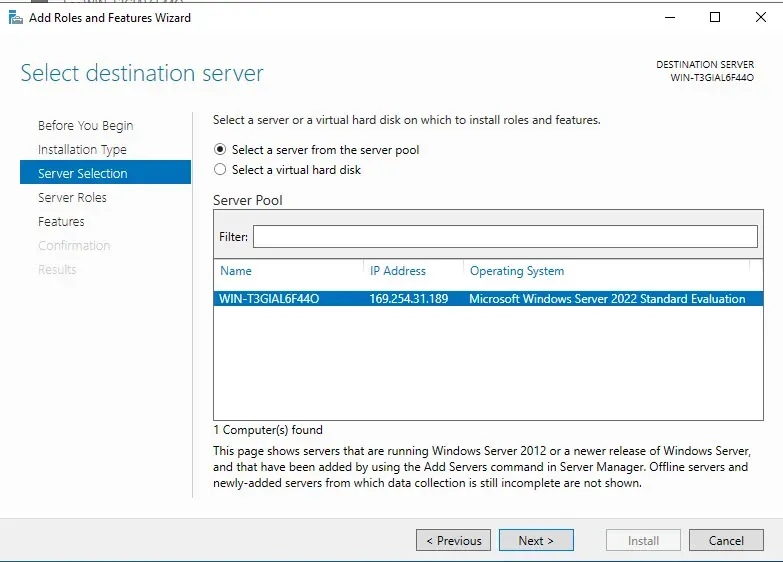
Next, we will select our destination server - essentially, what server are we applying these changes to?
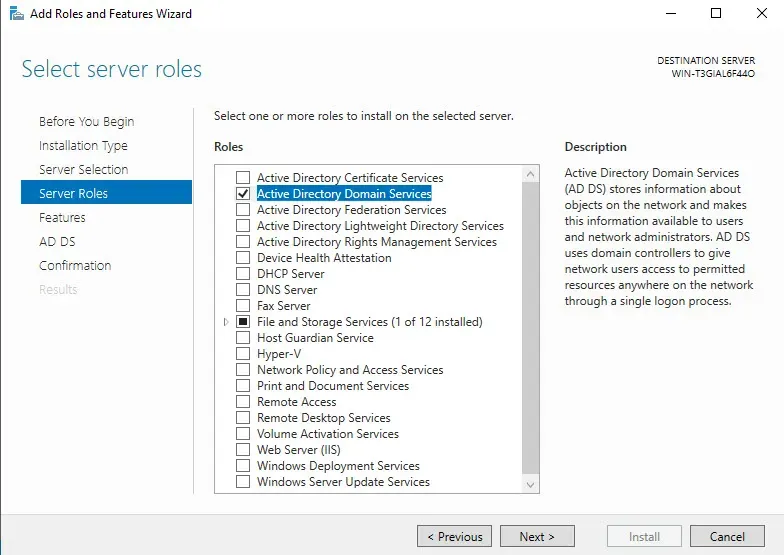
Next Server Roles, we will select "Active Directory Domain Services" -> Add Features and click Next.
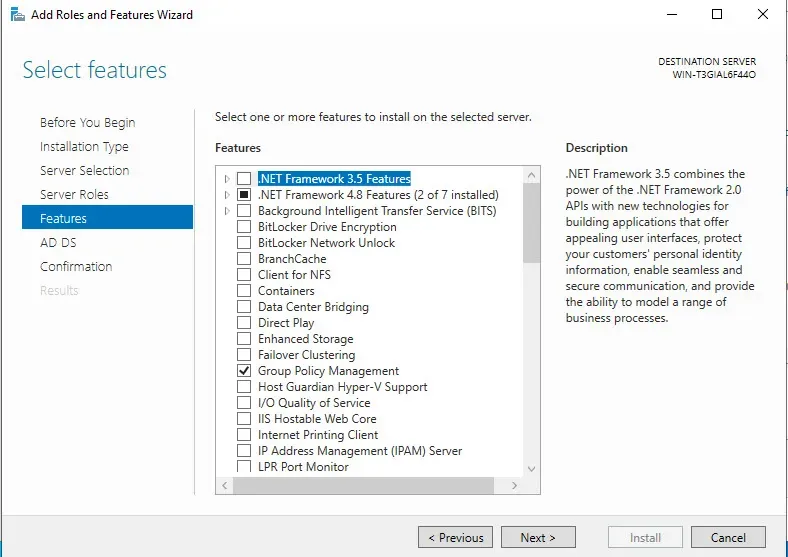
For features, we are going to skip and click next.
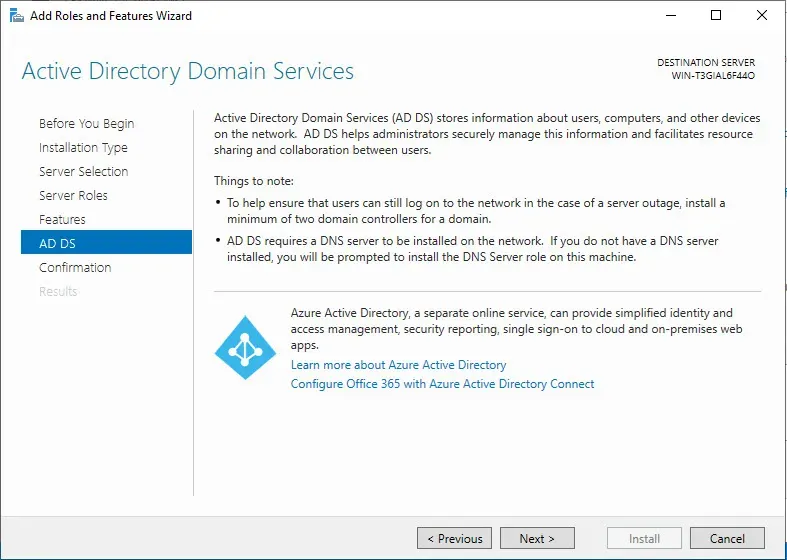
Active Directory Domain Services: -> Next.
Check: "Restart the destination servicer automatically if required" -> Install.
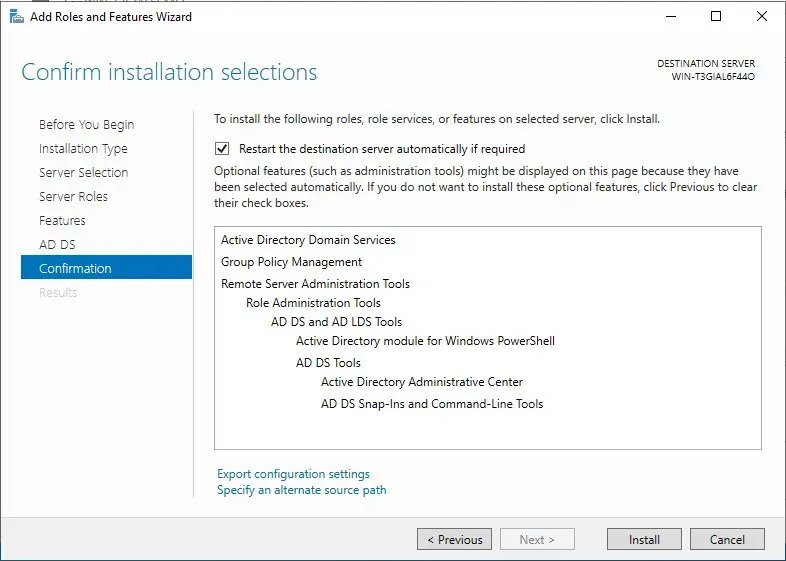
After the installation is done, we can click close.
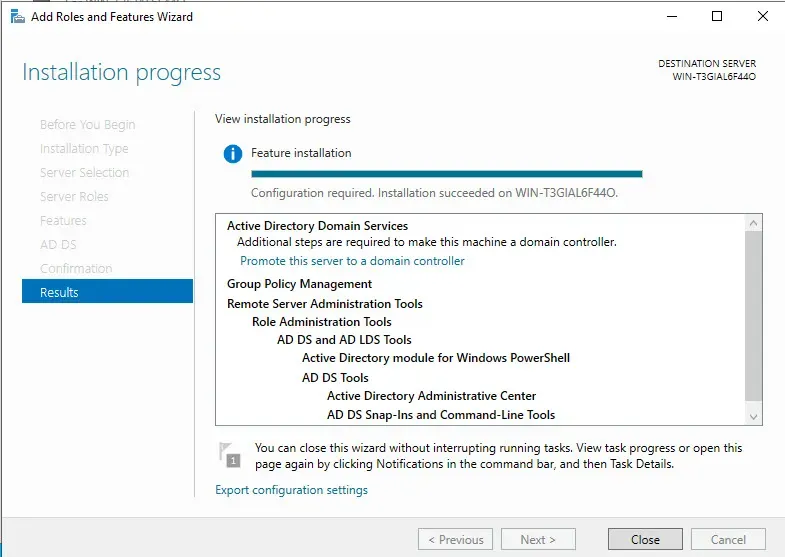
Step 2: Promote Server to Domain Controller
Your server manager should have a flag with a yield sign. Click on the yield sign, and you should see the text "Promote this server to a domain controller." Click the text.
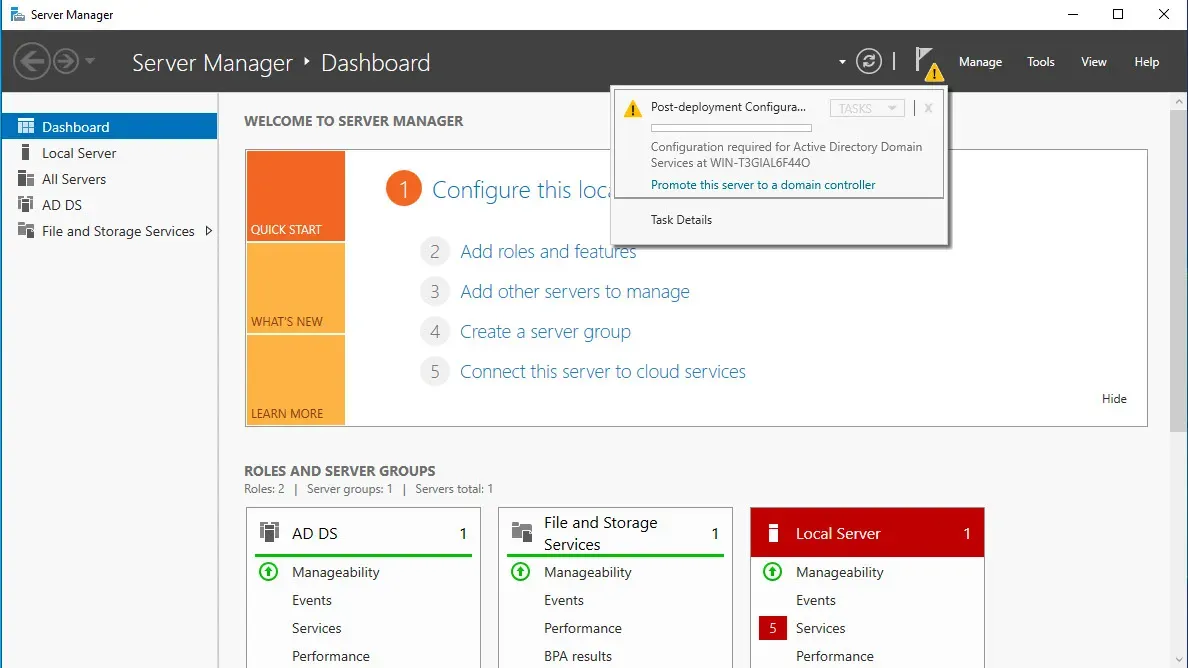
After you click the text, the Active Directory Domain Services Configuration Wizard will appear.
In this menu, we will create our domain.
First, we will select the third option: "Add a new forest."
Then, I will name my root domain securitynguyen.com. You can also name the domain something else and click "Next."
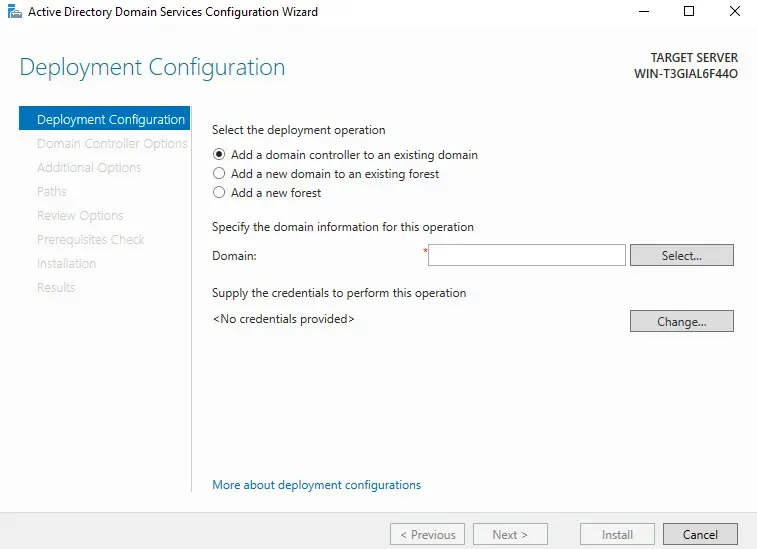
The next section is Domain Controller Options.
For the Forest and Domain Functional Levels, I will choose "Windows Server 2016." If I want my Domain controller to become a "DNS Server," I will leave that option checked. For now, I'll leave it as it is.
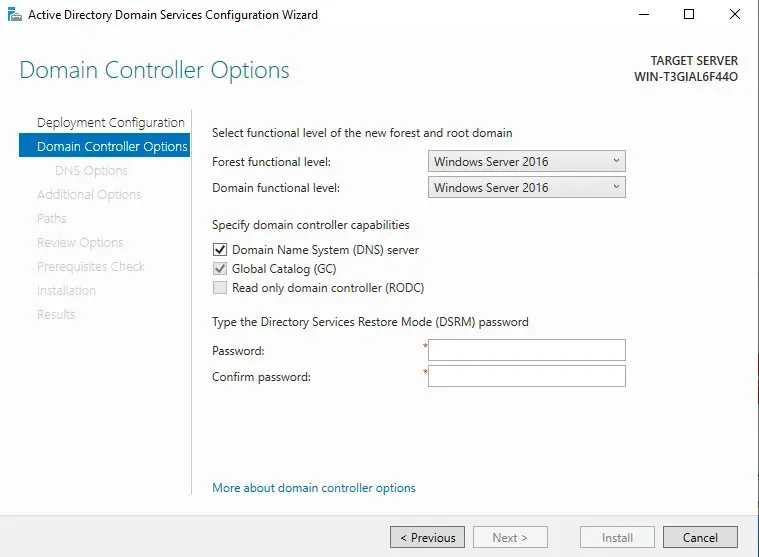
Then, for "Directory Services Restore Mode," assign any password.
Next is DNS Options; this section has nothing to do. We will click Next.
Next is Additional Options; I'm just going to click Next.
Next, the setup will ask where you want to store the Active Directory Database, Log Files, and SYSVOL. I'm just going to keep the default setting.
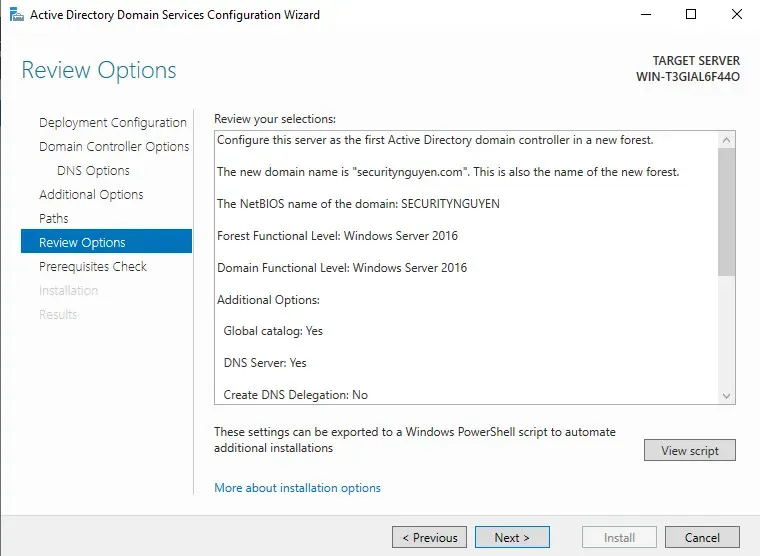
Next, Active directory will show you all the changes being made.
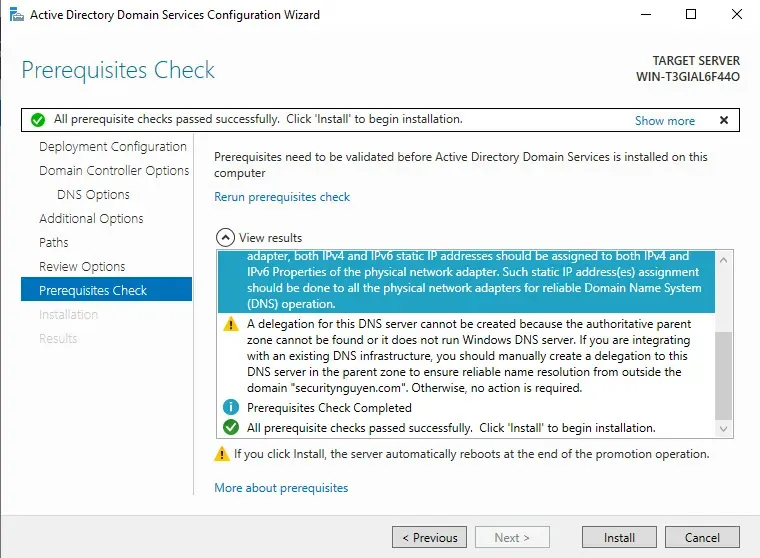
Then, Active Directory will check whether your Windows Server is ready for installation. After Active Directory finishes checking your Windows Server, click Install.
After installation, your Windows server should restart, and a log menu with the domain name should appear. As shown below.
Congratulations! You started a domain on your Windows Server.
