Analyzing Malicious Email - Phishing Analysis #1
Source:
InfoSec Handlers Diary Blog - SANS Internet Storm Center
https://isc.sans.edu/diary/October+2021+Contest+Forensic+Challenge/27960
October 2021 Contest: Forensic Challenge, Author: Brad Duncan
Malware-Traffic-Analysis.net - 2021-10-22 - Files for an ISC diary (October 2021 Forensic Contest)
https://www.malware-traffic-analysis.net/2021/10/22/index.html
Malicious Emails can be found above ☝️☝️
2021-10-21-malicious-email-1102-UTC.eml
Email header:
|
|
The processes of analyzing phishing emails:
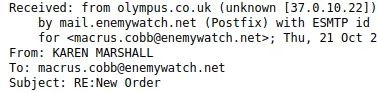
- Was the email sent from the correct SMTP server?
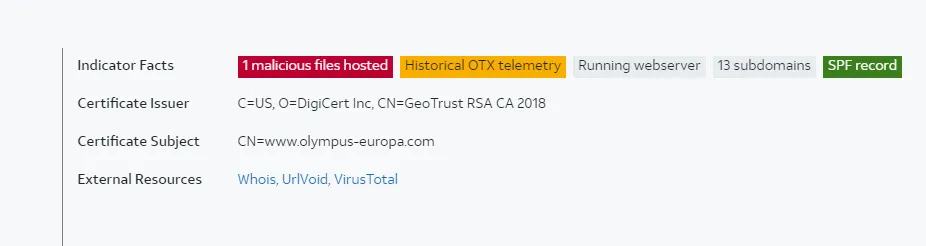
For instance: The person who sent the email was from: olympus.co.uk
I would pull up the MX toolbox and search: olympus.co.uk.
The IP of the olympus.co.uk (104.47.56.110)

Then I would compare the IP that I have in my email.
If the IP doesn’t align, that’s a sign that the email got spoofed.
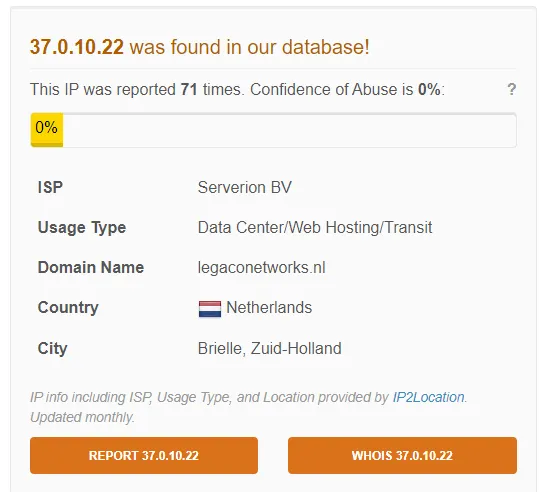
In this case, IP is 37.0.10.22, which tells us that the address was spoofed. That’s a red flag.
2. Are the data “From” and “Return-Path / Reply-To” the same?
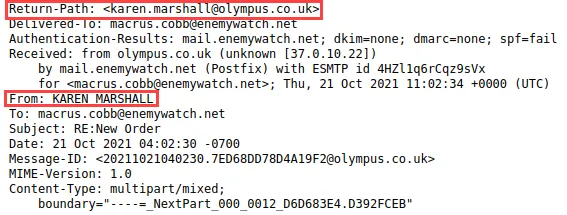
In this case, yes.
3. Look up the IP that it was sent from.
For this case, the IP was flagged as malicious in virus total.
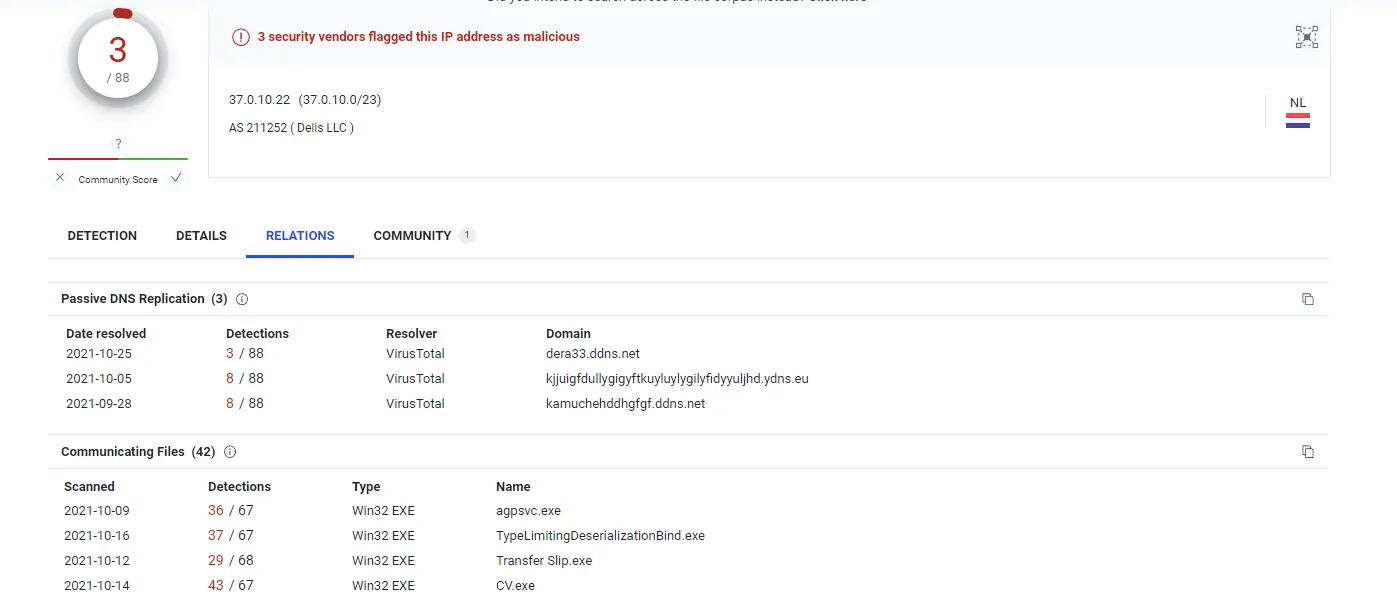
VirusTotal, AbuseIPDB, and AlienVault are indicating that the IP is malicious
4. Are there any grammar mistakes?
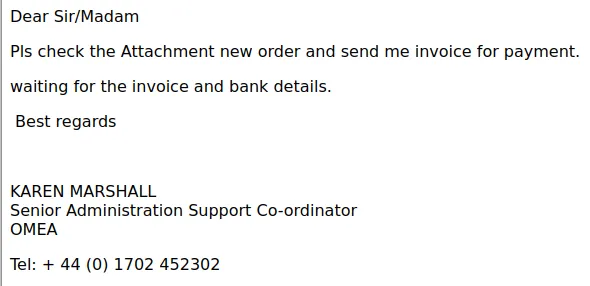
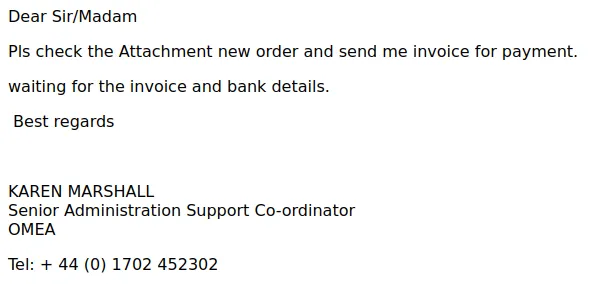
The use of Co-ordinator instead of coordinator and PLS instead of “please”.
Down under the job title of Karen Marshall, I’m assuming OMEA is a company and that the adversary forgot to change it to olympus.co.uk. The story doesn’t add up.
5. Suspicious Attachments
Attachments in a legitimate email are usually alluded to within the body. The sender may say, for instance, “I am attaching the report.” This makes it easy to check the attachment because its name should correlate with what was mentioned in the message.
With a phishing email, the attachment may have nothing to do with the contents of the body of the email. It may also be unnecessary—for example, an email about a report but with an attachment containing instructions on resetting your password.
Source: Fortinet
For this email, the attachment fits the story of the body.
6. Usually, in an Isolated environment, I would download the attachment, get the hash value of the attachment, and plug the hash into an OSINT website.
In this case, MD5 hash of Order.7z is 734e991a781c52b6441526029efa8da1
https://www.virustotal.com/gui/file/c7b83c5b3ab7114127fac61933145960b3b4e580eeab2f88eb31880fa447b910

Hybrid Analysis:
https://www.hybrid-analysis.com/sample/5bf04dc0a6c58392ab02344da78d8cf471f522f94a845974f33dac13a1e51af2/6186eaf1c76b4005501f68d4
Second Malicious Email
2021-10-21-malicious-email-1739-UTC.eml
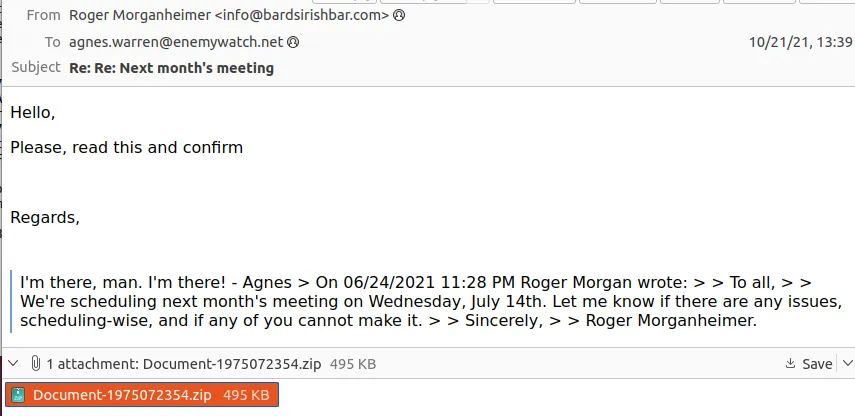
Email Header:
|
|
The process:
- Was the email sent from the correct SMTP server?
- Are the data “From” and “Return-Path / Reply-To” the same?
- Look up the IP that the email was sent from.
- Are there any grammar mistakes?
- Analyze the attachments
Was the email sent from the correct SMTP server?
I tried looking up bardsirish.com, but there’s no site record.
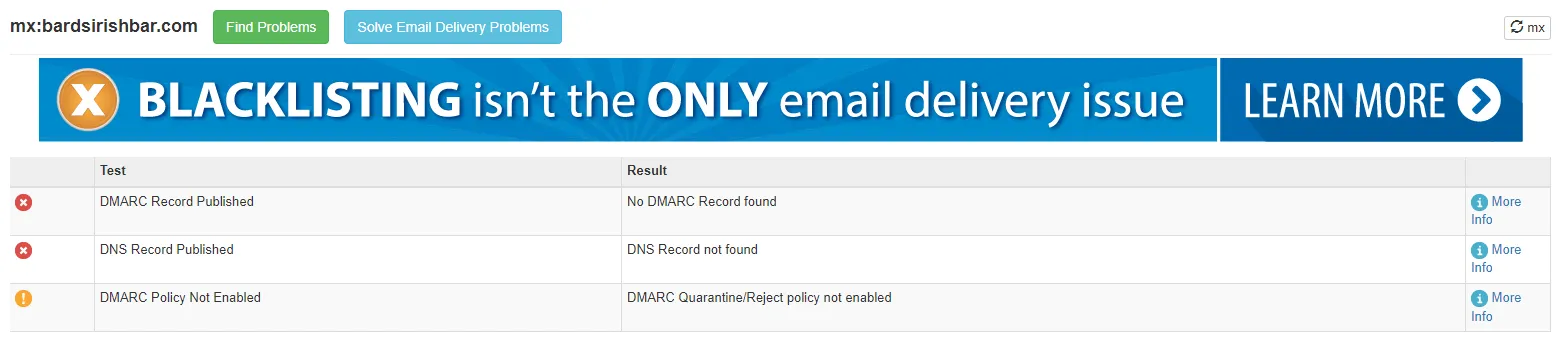
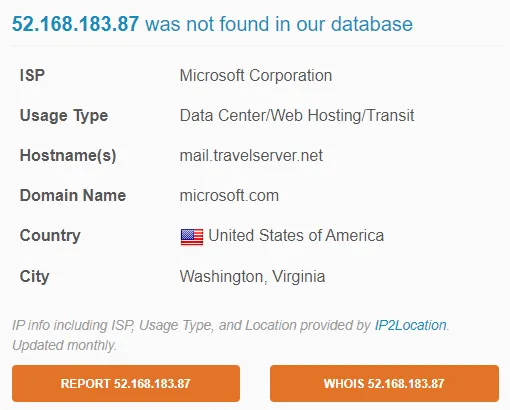
Additionally, if we look at the Received Section, the email came from: mail.travelserver.net [52.168.183.87].
bardsirishbar.com is an entirely different domain than mail.travelserver.net. For me, that’s a red flag.
Are the data “From” and “Return-Path / Reply-To” the same?
From: "Roger Morganheimer" info@bardsirishbar.com
Return Path: info@bardsirishbar.com
Result: Yes
Look up the IP that the email was sent from
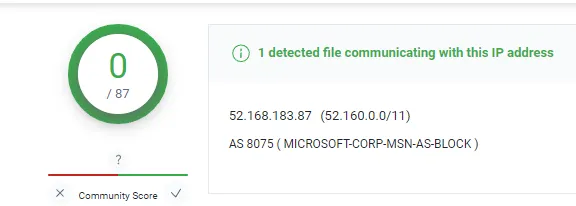
mail.travelserver.net [52.168.183.87]
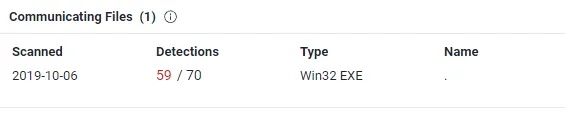
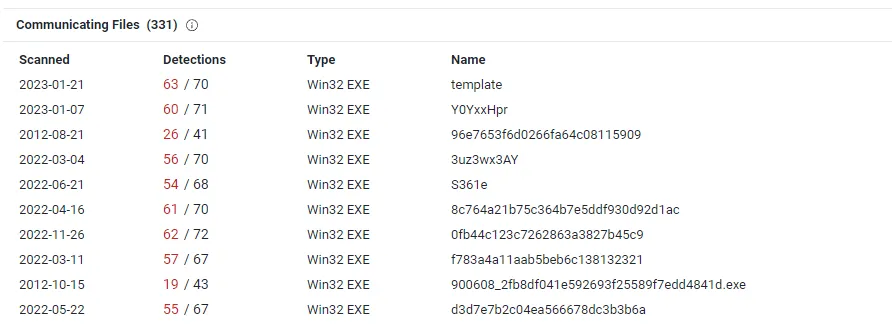
According to VirusTotal, the domain is clean. However, a malicious WIN32 executable has been communicating with the domain since 2019-10-06.
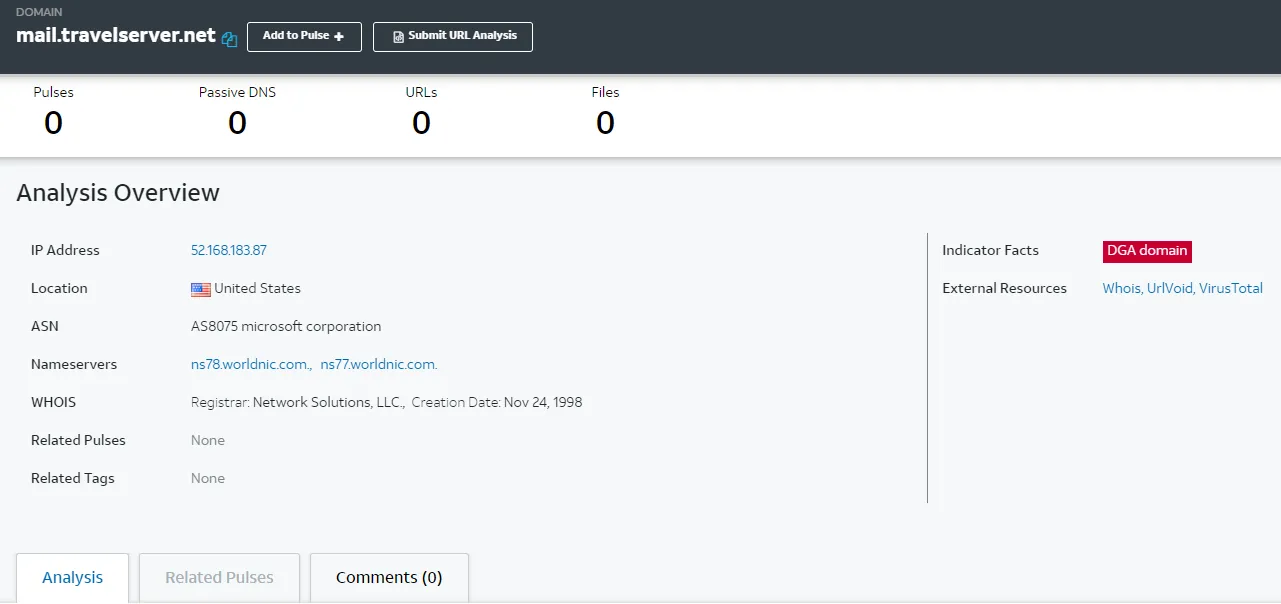
Even though none of the OSINT websites flag the domain as malicious, there were executables communications to the domain, which raises suspicion.
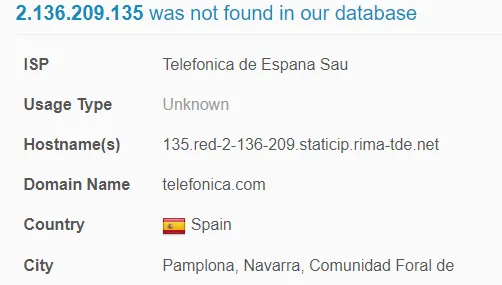
2.136.209.135
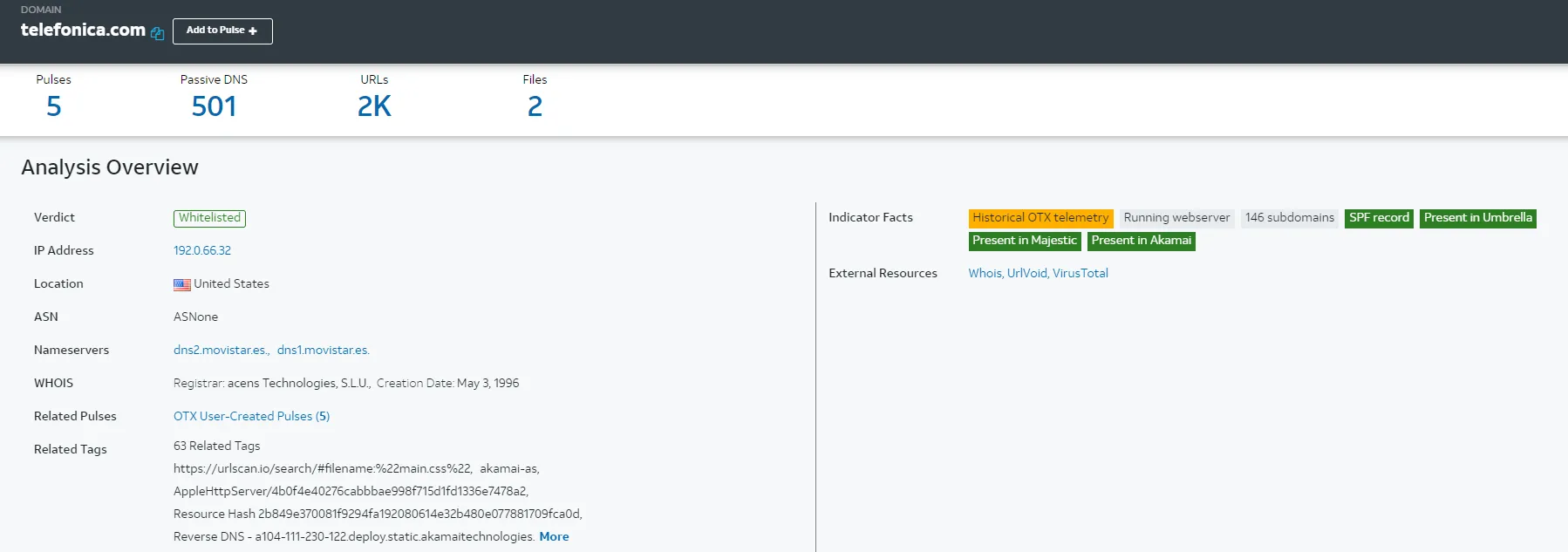
However, if you look up the actual domain…
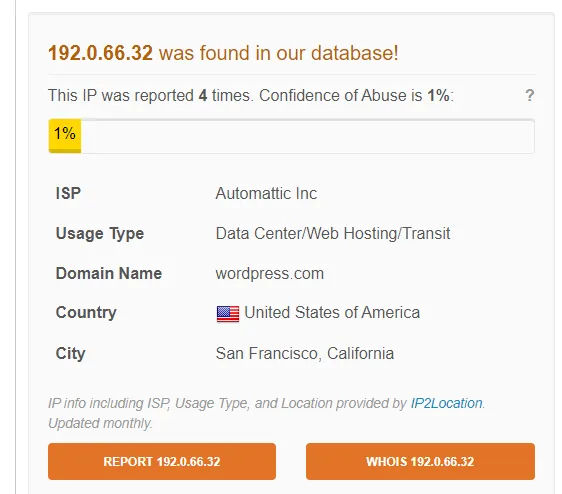
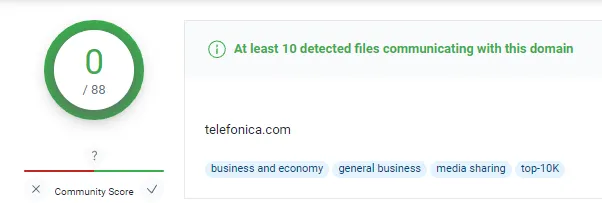
Even though the domain is clean on alien vault. AbuseIPDB and VirusTotal saw the domain as malicious, and a bunch of malicious files was communicating with telefonica.com
Are there any grammar mistakes?
Nope, I don’t see any grammar mistakes.
Analyze the attachments
VirusTotal https://www.virustotal.com/gui/file/705166d5a107122554448752482515ac0a4a6aeffcdd668625db55d9f84f2af4
MD5: 8a184c701108cb94056055da8f026db7

According to VirusTotal, inside the .zip file is an excel spreadsheet with a malicious macro.
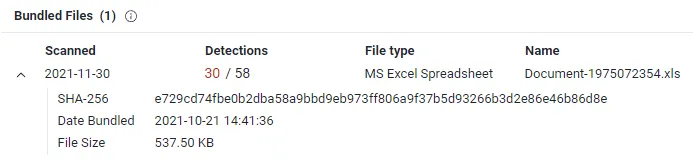
Result:
After going through the process and especially analyzing the attachment, I can surely say this email is malicious.
Third Malicious Email
Was the email sent from the correct SMTP server?
There’s no mail server for enemywatch.net
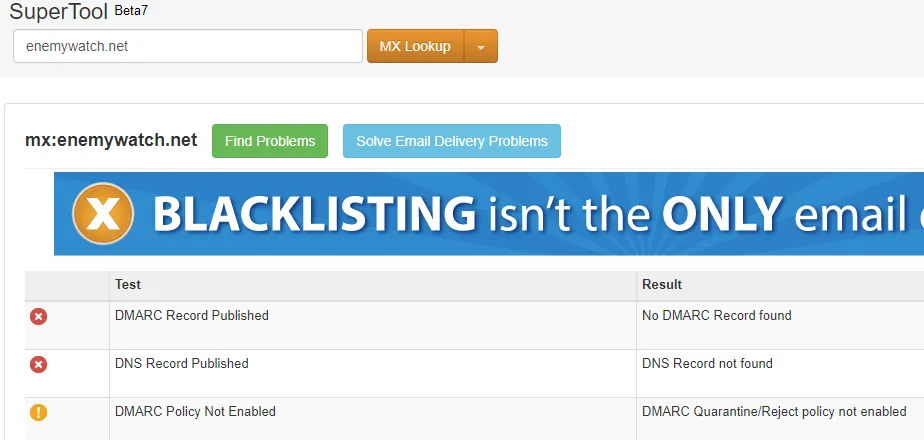
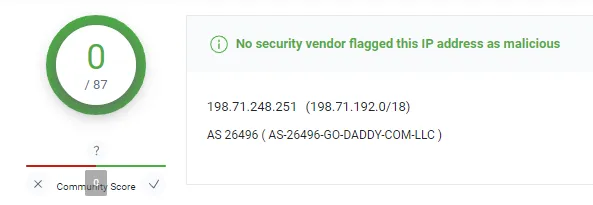
But the email came from 198.71.247.251, which is an email server.
Are the data “From” and “Return-Path / Reply-To” the same?
From: Enemy Watch webmaster@enemywatch.net
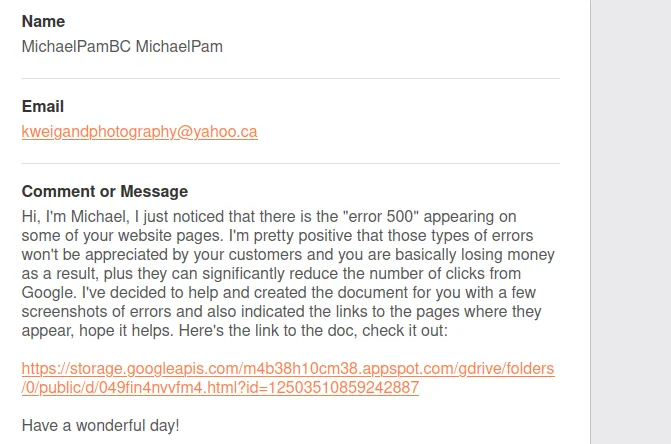
Return-Path: webservices@webserver.enemywatch.net
Reply To: kweigandphotography@yahoo.ca
The data from the “FROM” field match with “Return-Path”. But the “reply-to” is entirely different, primarily the domain. Instead of o com, it’s yahoo.ca
Look up the IP that the email was sent from
Are there any grammar mistakes?
No grammar mistakes.
Analyze the attachments
For this email, instead of having attachments in the email, there’s a link.
According to VirusTotal, the URL is malicious.

Conclusion:
This malicious mail was well written. However, the thing that gave it away was the link.
The link redirects to stoage.googleapis.com. But if you were sharing a document with someone, why would you share a link that goes to googleapis and not google drive?
Furthermore, the “reply-to” email address was yahoo.ca instead of yahoo.com, which is a red flag. This is an example of TypoSquatting.